 PNRA_IPEV
PNRA_IPEVWhat is probably the world’s oldest ice, dating back 1.2m years ago, has been dug out from deep within Antarctica.
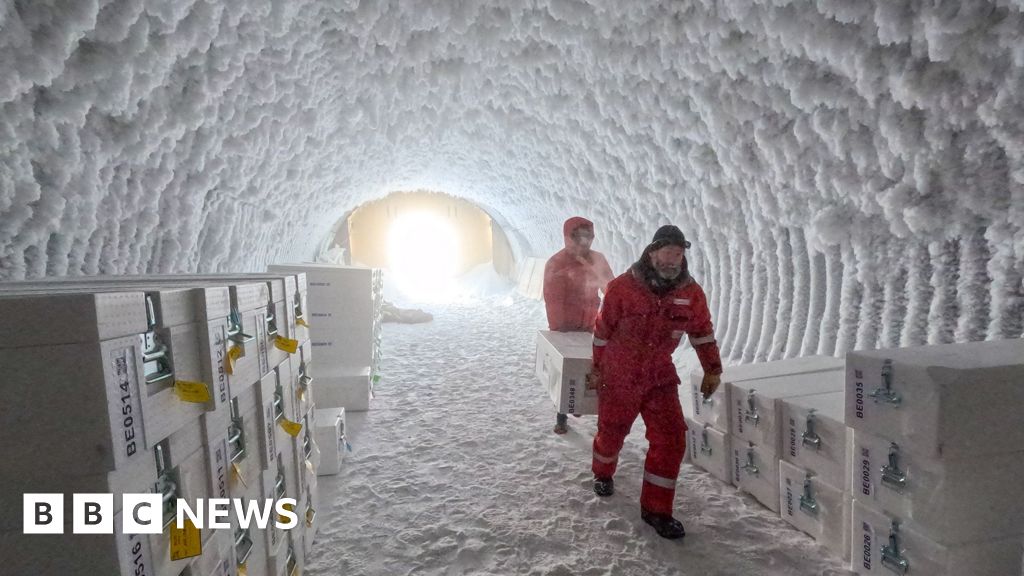
Working at temperatures of -35C, a team of scientists extracted a 2.8km-long cyclinder, or core, of ice – longer than eight Eiffel Towers end-to-end.
Suspended inside the ice are ancient air bubbles which scientists hope will help solve an enduring mystery about our planet’s climate history.
The European scientists worked over four Antarctic summers, racing against seven nations to be first to reach the rock under the frozen continent.
 PNRA_IPEV
PNRA_IPEVTheir work could help unravel one of the major mysteries in our planet’s climate history – what happened 900,000-1.2 million years ago when glacial cycles were disrupted and some researchers say our ancestors came close to extinction.
“It’s an amazing achievement,” says Prof Carlo Barbante at Ca’ Foscari University of Venice who co-ordinated the research.
“You have in your hands a piece of ice that is a million years old. Sometimes you see ash layers coming from volcanic eruptions. You see the tiny bubbles inside, some bubbles of air that our ancestors breathed a million years ago,” he says.
The team was led by the Italian Institute of Polar Sciences and included 10 European nations.
 PNRA_IPEV
PNRA_IPEVIt had to transport the drilling equipment, laboratories and camp 40km by snow mobiles from the nearest research base.
The drilling site, called Little Dome C, is on the Antarctic plateau on the east of the continent, at almost 3000m elevation.
Ice cores are a vital to scientists’ understanding of how our climate is changing.
They trap bubbles of air and particles that reveal levels of greenhouse gas emissions and temperature variation that help scientists plot how climatic conditions have altered over time.
Data from other ice cores, including one called Epica, helped scientists conclude that the current rise in temperature linked to greenhouse gas emissions is caused by humans burning fossil fuels.
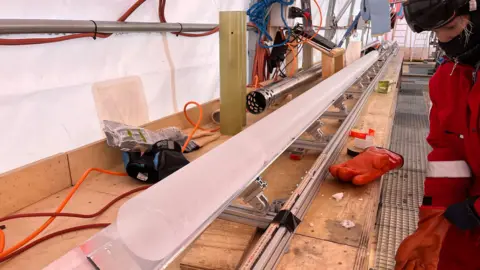 PNRA_IPEV
PNRA_IPEVBut scientists wanted to go further back in time.
Now with this project Beyond Epica: Oldest Ice they have gained potentially another 400,000 years of history.
“There is a lot of the past in our future. We look at the past to understand better how the climate works and how can we project it into the future,” says Prof Barbante.
The team had a “nail-biting last few days” as they were able to drill even deeper than anticipated from radar data, says Dr Robert Mulvaney, an ice core scientist at British Antarctic Survey.

The core was slowly pulled from the ice sheet using a drill machinery and scientists carefully cleaned the ice using cloths.
It is now being cut into one metre pieces for transportation at -50C from Antarctica by boat.
The pieces will eventually reach the freezers of numerous European institutions, including the British Antarctic Survey in Cambridge, where scientists will begin their analysis.
Experts want to understand what happened in a period 900,000 to 1.2 million years ago called the Mid-Pleistocene Transition.
At this time, the length of the cycle between cold glacial and warm interglacials switched from being 41,000 years to 100,000 years. But scientists have never understood why.
This is the same period when, according to some theories, the ancestors of present-day humans almost died out, perhaps dropping to around just 1000 individuals.
Scientists do not know if there is a link between this near-extinction and the climate, explains Prof Barbante, but it demonstrates it is an unusual period that it is important to better understand.
“What they will find is anybody’s guess but it will undoubtedly enlarge our window on our planet’s past,” Professor Joeri Rogelj from Imperial College in London, who was not involved in the project, told BBC News.
Follow Georgina on BlueSky.


